An IP address is a unique number or alphanumeric code that is linked to a device or router. It facilitates the proper direction of internet traffic. An IP address and your postal address are equivalent in real life. It facilitates mail delivery to the intended recipient by the postal service. Although most users know what an IP address is, many are unaware that there are two different types.
There are two types of IP addresses: private and public. Both are essential for accessing the internet. This article describes the differences between private and public IP addresses. We explain the advantages of each type and demonstrate how you can use them to safeguard your online activities, ensuring privacy and security.
IP Address
An IP address, or Internet Protocol address, is a special number allocated to a computer network to facilitate communication across the protocol. 192.0.2.1 is an example of an IP address. An IP address is used to identify a host or network interface and to address a specific location. The two functions of an IP address are to identify the host, or more precisely, its network interface, and to display the host’s location inside the network so that a path may be constructed to reach it.IP addresses may be private or public.
Public IP Address
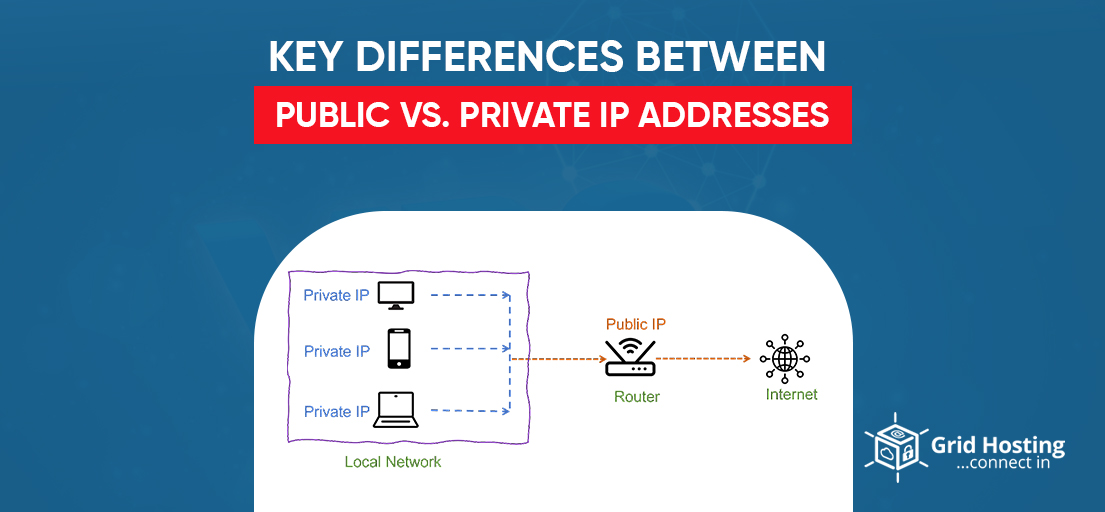
Your network router has a public IP address assigned to it by your Internet service provider (ISP), making it instantly accessible over the Internet. Your device’s private IP address is concealed when you connect to the internet using your router’s public IP address. When you connect to the internet using a public IP address, it’s like sending letters to a P.O. box rather than your home address. It’s much more evident, but it’s a little safer.
Private IP Address
The address that your device gets from your network router is known as a private IP address. To enable communication, every device connected to the same internal network is assigned a distinct private IP address, sometimes referred to as a private network address. Devices connected to the same network can communicate with one another without connecting to the internet thanks to private IP addresses. By making it harder for an outside host or user to join, private IPs help to improve security within a specific network, such as your home or place of business. This means that although you can print documents wirelessly from your home printer, your neighbor cannot inadvertently send files to your printer.
Key Differences Between Public and Private IP Addresses
Public vs Private Addresses: Unveiling the Distinctions
Within the complex field of computer networking, the distinction between public and private addresses is crucial in determining how data moves across the internet. Anyone navigating the complex network of IT infrastructure and connection has to be aware of these distinctions. Let’s examine the salient distinctions between public and private addresses and explore the nuances around their application.
Public Addresses: Bridging the Global Divide
Internet service providers (ISPs) or regional Internet registries assign public addresses, which are the foundation of worldwide connectivity. These addresses are globally unique identifiers that enable communication over the vast expanse of the internet. They frequently function under the Internet Protocol versions 4 (IPv4) or 6 (IPv6).
Public addresses are limited resources that are scarce by nature. with the dwindling pool of available IPv4 addresses necessitating the industry’s transition to IPv6. Websites, servers, and any device requiring direct accessibility from the internet rely on public addresses. These addresses are associated with specific geographical locations and are the gateway to worldwide connectivity.
Private Addresses: Localized Networks and Intranet Dynamics
Contrasting with their globally exposed counterparts, private addresses find their domain within local networks, whether in homes or businesses. These addresses are not globally unique, allowing multiple networks to employ the same private address ranges without conflict. The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) reserves the most common private address ranges, providing a standardized framework for internal communication.
Within local networks, devices communicate using private addresses, fostering an environment insulated from direct exposure to the vast internet. The implementation of Network Address Translation (NAT) devices manages the translation between private and public addresses when data needs to traverse the internet. This ingenious system enables multiple devices within a local network to share a single public address, mitigating the scarcity of public addresses.
Security and Accessibility: Balancing Act
A critical differentiator between public and private addresses lies in their security implications and accessibility. Public addresses, being globally accessible, are inherently more susceptible to security risks. Devices with public addresses must implement robust security measures to fend off unauthorized access and potential cyber threats originating from any corner of the internet.
The use of private addresses offers an inherent layer of security. Devices within a local network, shielded by NAT devices, are not directly reachable from the internet. This intrinsic protection adds a barrier against external threats, providing a level of security beneficial for internal network communications.
Scalability and Management: Navigating the Administrative Terrain
The management of public addresses involves a complex administrative process, requiring coordination with ISPs or internet registries. This process incurs administrative overhead and potential costs, particularly as the demand for internet-connected devices surges. The transition to IPv6 becomes imperative to overcome the limitations posed by the exhaustion of IPv4 addresses.
In contrast, private addresses managed locally, offer a more flexible and scalable solution within a specific network. Network administrators wield greater control over the allocation and configuration of private addresses, simplifying the management of internal devices. This localized control enhances scalability and adaptability, critical factors in the ever-evolving landscape of network dynamics.
Future Perspectives: Public and Private Addresses in the Evolving Digital Horizon
As the digital world advances, the distinction between public and private addresses will become more and more significant. The ongoing transition to IPv6, the rise of edge computing, and the spread of Internet of Things (IoT) devices will alter the dynamics of address allocation and administration. A forward-thinking strategy will be necessary to navigate this changing landscape and maintain networks’ resilience, security, and ability to adjust to changing needs.
The divergence between public and private addresses lies in their scope, accessibility, security implications, and administrative management. Public addresses bridge the global connectivity divide, while private addresses provide a secure and scalable framework for internal communications. As the digital era unfolds, a nuanced understanding of these address types becomes paramount for network administrators and IT professionals steering the course of interconnected systems.
Read More: What to look for, while selecting any web hosting company?
Conclusion
Public and private IP addresses are the two primary types. Your internet service provider (ISP) will assign your network a public IP address, which is necessary for internet access. Conversely, a private IP address is specifically assigned to your device by your network router. The main difference between these two IP addresses is that, by connecting your device to the internet, the public IP address allows you to access all the information you need.it is common practice to connect directly and securely to other devices within the private network using a private IP address.
Grid Hosting’s Secure VPN service provides a highly secure way of using the internet. By using shared IP addresses, your online activities are hidden and it prevents others from tracking you. You can access the internet from anywhere in the world while ensuring that your data remains protected. You can sign up for a free trial and experience all the benefits of Grid Hosting’s Secure VPN service.
For Special discounts and offers, visit our official Facebook Page